RADAR can be run on the command line by following the instructions on the Docs page or through the web here. Running RADAR through the website will print the results after several moments. You can try running RADAR through the web form with a sample file with one variant. Alternatively, you may also input a list of variants into the form as text. If variants are provided in both file and text formats, the variant file will be scored and the text field will be ignored.
More details on the RADAR inputs can be found on the Docs page.

Download RADAR and all necessary resource files in a ZIP format here (1.5 GB).
For Python 3 compatibility see here.
The following software are required to run RADAR.
1) BEDTools
2) Python (Python 2 or 3 compatible)
3) pybedtools
4) vcf2bed
All required data resources are contained in the resources/ directory of the RADAR package.
Download Significant peaks (significant_peaks, text file, 95 MB)
Matrix representing whether an RBP peak overlaps a significant gene in a cancer type. Rows are labeled by RBP peaks, columns by cancer type. A value of 1 indicates the peak overlaps a significant gene in this cancer, else 0. Used to compute the key genes score.
Download RBP binding site data (all_RBP_peaks_unmerged_labeled_sorted.bed, BED file, 42 MB)
A BED file containing all RBP peaks considered. Each line represents one peak and is formatted as: chromosome, start, stop, RBP.
Download RBP peak mutational burden data (rbp_peak_significance, text file, 95 MB)
Mutational burden data for each RBP binding peak with respect to Alexandrov variants in 30 different cancer types. Each line represents an RBP binding peak. A line is tab-delimited and formatted as: chromosome, start, stop, RBP, then 30 values indicating whether this peak is burdened in each cancer (sorted alphabetically, 1 indicates it is burdened, 0 if not).
Download RBP regulatory power data (regulator_pval.txt, text file, 5 KB)
Matrix representing whether an RBP exhibits strong regulatory power in a cancer type. Rows are labeled by RBP, columns by cancer type. A value of 1 indicates high regulatory power, else 0.
Download Precomputed universal scores, hg19 (hg19/, zip archive, 768 MB)
Directory containing files, one for each chromosome. Each file contains precomputed universal scores for every single position and possible alternate allele in the regulome. RADAR looks up scores from these tables instead of recomputing them on the spot.
Download Precomputed universal scores, hg38 (hg38/, zip archive, 731 MB)
hg38 Version of the precomputed scores.
Supplemental Data Files
Download Non-splicing RBP peaks (non_splicing/, zip archive, 6.4 MB)
Directory containing RBP peak files for all RBPs not involved with splicing. Not necessary for RADAR.
Download Splicing RBP peaks (splicing/, zip archive, 4.5 MB)
Directory containing RBP peak files for all RBPs involved with splicing. Not necessary for RADAR.
Supplemental Table Files
Download Supplementary Table (supplement tables, xlsx file, 2.2 MB)
Tables from supplement of RADAR.
FunSeq2
Variants that do not fall in the RBP regulome as defined by the eCLIP peaks can be scored using FunSeq2. Whole genome scores can be found at FunSeq2 downloads page.
Table of Contents
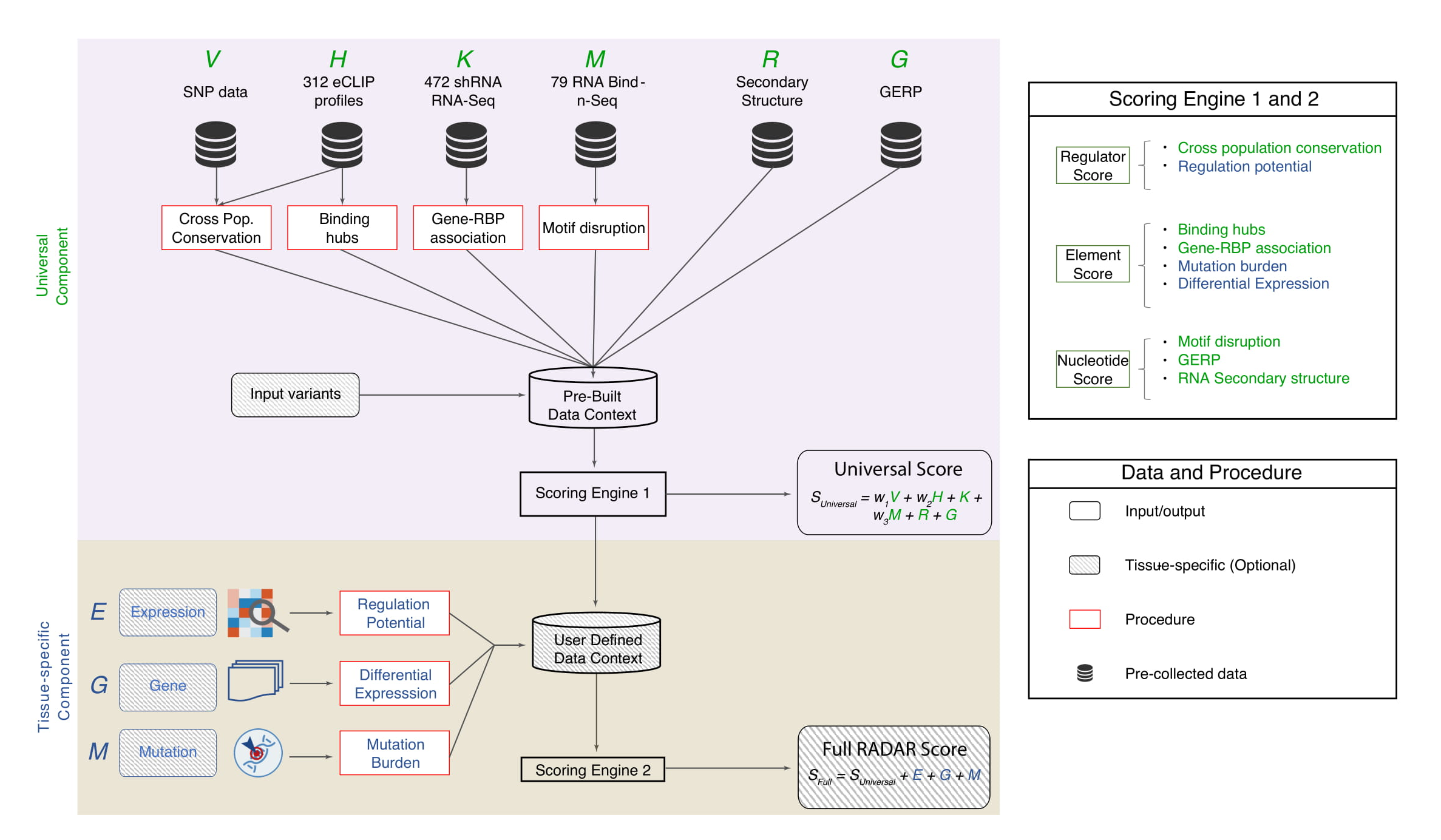
Usage Overviewpython radar.py -b <variant BED file> -o <output directory> -a [assembly] -c [cancer type] [-kg -mr -rp]
Two parameters are required by RADAR: a BED file containing the variants to be scored, and an output directory where the scores will be written to. Each line of the input should be formatted as: chromosome, start, stop, reference allele, alternate allele. The output is a BED file with the scored variant, each line formatted as: chromosome, start, stop, reference allele, alternate allele, cross-species conservation score, hub score, GERP score, RNA structure (EvoFold score), motif disruption score, RBP-gene association score, total universal score, [key genes score], [mutation recurrence score], [regulatory power score], total tissue-specific score, total score. Scores in brackets [] are tissue-specific scores, and can be optionally included; the other scores are provided by default.
The -a flag may optionally be provided to specify which genome assembly to use for scoring. hg19 and hg38 are currently supported (hg19 is selected by default). Tissue-specific scores are only compatible with hg19.
If the -kg flag is provided the key genes score will be included, and each variant will also be scored based on whether it falls in an RBP binding peak that overlaps a significant gene in the given cancer type.
If the -mr flag is provided, the mutation recurrence score will be included, and each variant will also be scored based on whether it falls in a mutationally burdened RBP binding site with respect to Alexandrov variants from the given cancer type.
If the -rp flag is provided, the regulatory power score will be included, and each variant will also be scored based on whether it falls in the binding peak of an RBP with high regulatory power in the given cancer type.
If any of the three optional tissue-specific scores are requested, a cancer type must also be provided following the -c flag. RADAR currently supports 19 TCGA cancer types for the above three options: BLCA, BRCA, CESC, COAD, ESCA, GBM, HNSC, KICH, KIRC, KIRP, LIHC, LUAD, LUSC, SKCM, PAAD, PRAD, STAD, THCA, UCEC.
The variant BED file should be tab-delimited: chr, start, stop, reference allele, alternate allele. Extra columns are ignored.
RADAR outputs a single tab-delimited BED file in the provided output directory. The file contains a header to describe each column. Each row after the header represents a single variant (chr, start, stop, reference allele, alternate allele) followed by the requested scores. The order of variants in the output is the same as the order provided in the input BED file.
The following are detailed step-by-step guides on how to score a set of variants using RADAR from start to finish.
First, download the required software: BEDTools, Python (our tests were conducted with Python version 2.7), and pybedtools. Follow the installation instructions for each one. You can confirm you have successfully installed each piece of software by attempting to run bedtools on the command line, which should print out documentation for BEDTools like so (output is truncated):
bedtools is a powerful toolset for genome arithmetic.
Version: v2.27.1
About: developed in the quinlanlab.org and by many contributors worldwide.
Docs: http://bedtools.readthedocs.io/
Code: https://github.com/arq5x/bedtools2
Mail: https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/bedtools-discuss
Usage: bedtools <subcommand> [options]
You can confirm you have Python and pybedtools installed by running the Python shell using the python command and attempting to import the pybedtools module with import pybedtools. If there are no errors, the prerequisite software was installed successfully. Note the Python version number on the first line after running the python command.
$ python
Python 2.7.13
[GCC 5.4.0] on linux2
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import pybedtools
>>>
Next, download the RADAR package in ZIP format from the RADAR website Downloads page Unzip the file at the command line (using unzip radar.zip. After unzipping, you should see a directory called radar/ containing two items: a .py file (the executable script) and a resources/ directory that contains all data files needed by the RADAR script to produce scores.
Here is a head of the example input file we will be using (publicly accessible data from Alexandrov et al breast cancer variants). This file (called Breast.bed) is downloadable from the Example page. (You may also like to follow along with a shorter version of this BED file, containing only the first 100 variants, called Breast_100.bed.)
chr1 13506 13507 G A TCGA-EW-A1OZ-01A-11D-A142-09
chr1 14841 14842 G T PD5935a
chr1 16995 16996 T C PD7201a
chr1 17764 17765 G A PD5935a
chr1 17764 17765 G A PD7216a
chr1 28587 28588 G T PD4962a
chr1 30527 30528 C T PD5935a
chr1 61396 61397 G A PD4967a
chr1 69522 69523 G T TCGA-BH-A0BP-01A-11D-A10Y-09
chr1 83442 83443 C T PD4072a
Now we are ready to run the software and score our variants. Move into the recently unzipped radar/ directory, where the radar.py file exists (using cd radar/). Locate the path to the Breast.bed file (in the example command below, we will assume it exists in the parent directory of radar/). Also identify a directory into which you would like the output file to be written (in this example, we will write the output to the same directory that contains Breast.bed). Now, see the following 5 walkthroughs to see how to run RADAR for different use cases. Note that a cancer type must be specified if at least one tissue-specific score is requested. (We use BRCA here, since we are scoring breast cancer variants, but any of the TCGA cancer types listed above are valid.) In any case, RADAR will generate the output file in the specified output directory. The file will be called Breast.radar_out.bed in this case, and will contain the list of scored variants.
1) Running RADAR without tissue-specific scores
To score this set of variants without any tissue-specific scores, run the following command:
python radar.py -b ../Breast.bed -o ..
A head of the output file is shown below:
chr start stop ref alt cross_species_conservation RBP_binding_hub GERP Evofold motif_disruption RBP_gene_association total_universal total_tissue_specific total_score
chr1 13506 13507 G A 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 14841 14842 G T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 16995 16996 T C 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 17764 17765 G A 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 28587 28588 G T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 30527 30528 C T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 61396 61397 G A 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 69522 69523 G T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 83442 83443 C T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
2) Running RADAR with the key genes score
To score this set of variants with the universal scores and the key genes score, run the following command:
python radar.py -b ../Breast.bed -o .. -c BRCA -kg
A head of the output file is shown below:
chr start stop ref alt cross_species_conservation RBP_binding_hub GERP Evofold motif_disruption RBP_gene_association key_genes total_universal total_tissue_specific total_score
chr1 13506 13507 G A 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 14841 14842 G T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 16995 16996 T C 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 17764 17765 G A 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 28587 28588 G T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 30527 30528 C T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 61396 61397 G A 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 69522 69523 G T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 83442 83443 C T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
3) Running RADAR with the mutation recurrence score
To score this set of variants with the universal scores and the mutation recurrence score, run the following command:
python radar.py -b ../Breast.bed -o .. -c BRCA -mr
A head of the output file is shown below:
chr start stop ref alt cross_species_conservation RBP_binding_hub GERP Evofold motif_disruption RBP_gene_association mutation_recurrence total_universal total_tissue_specific total_score
chr1 13506 13507 G A 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 14841 14842 G T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 16995 16996 T C 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 17764 17765 G A 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 28587 28588 G T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 30527 30528 C T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 61396 61397 G A 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 69522 69523 G T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 83442 83443 C T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4) Running RADAR with the RBP regulation power score
To score this set of variants with the universal scores and the RBP regulation power score, run the following command:
python radar.py -b ../Breast.bed -o .. -c BRCA -rp
A head of the output file is shown below:
chr start stop ref alt cross_species_conservation RBP_binding_hub GERP Evofold motif_disruption RBP_gene_association RBP_regulation_power total_universal total_tissue_specific total_score
chr1 13506 13507 G A 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 14841 14842 G T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 16995 16996 T C 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 17764 17765 G A 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 28587 28588 G T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 30527 30528 C T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 61396 61397 G A 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 69522 69523 G T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 83442 83443 C T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
5) Running RADAR with all tissue-specific scores
To score this set of variants with all scores (universal and all tissue-specific scores), run the following command:
python radar.py -b ../Breast.bed -o .. -c BRCA -kg -mr -rp
A head of the output file is shown below:
chr start stop ref alt cross_species_conservation RBP_binding_hub GERP Evofold motif_disruption RBP_gene_association total_universal key_genes mutation_recurrence RBP_regulation_power total_tissue_specific total_score
chr1 13506 13507 G A 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 14841 14842 G T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 16995 16996 T C 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 17764 17765 G A 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 28587 28588 G T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 30527 30528 C T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 61396 61397 G A 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 69522 69523 G T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
chr1 83442 83443 C T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Runtime was measured on three sets of variants: 100; 1,000; and 100,000 random variants from the Alexandrov breast cancer variants. 100 variants were scored in ~29 seconds; 1,000 variants were scored in ~32 seconds; and 100,000 variants were scored in ~34 seconds.
We provide an example of RADAR usage and output on the Alexandrov breast cancer variants. For a detailed walkthrough, please refer to the Docs page.
Input
Download the Alexandrov breast cancer variants here (25 MB).
...
chr1 979769 979770 G T PD8623a
chr1 984734 984735 A T TCGA-D8-A27M-01A-11D-A16D-09
chr1 985340 985341 G T TCGA-C8-A12W-01A-11D-A10Y-09
chr1 986796 986797 T G PD5935a
Command
The following command will run RADAR and produce an output file in the radar_output/ directory.
python radar.py -b Breast.bed -o radar_output/ -c BRCA -kg -mr -rp
Output
Download the output file generated from running the above command on the example Alexandrov breast cancer variants here (35 MB). (Note that the ellipsis denotes truncated lines; it is not in the output.)
chr start stop ref alt cross_species_conservation RBP_binding_hub GERP Evofold motif_disruption RBP_gene_association total_universal key_genes mutation_recurrence RBP_regulation_power total_tissue_specific total_score
...
chr1 985340 985341 G T 1.15940591176 0.0 4.53503723229e-33 0 1.11097289519 0 2.27037880695 1 1 0 2 4.27037880695
chr1 986796 986797 T G 1.07533132443 0.0 4.53503723229e-33 0 0 0 1.07533132443 1 1 1 3 4.07533132443
chr1 990581 990582 A C 1.11221704768 0.0 4.53503723229e-33 0 0 0 1.11221704768 1 1 0 2 3.11221704768
chr1 996865 996866 G T 1.12533280851 0.968597089781 4.53503723229e-33 0 0 0 2.09392989829 0 1 0 1 3.09392989829
Subset of Alexandrov data with high RADAR score
Alternatively, you can download a subset of the above breast cancer variants with high RADAR scores here.